The BRAID model
BRAID stands for Bridging Research, Accurate Information, and Dialogue
BRAID is an evidence-based biphasic model developed at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine. The model closely aligns with best practices in trustbuilding¹. The model represents a unique collaboration where clinical researchers, healthcare professionals, and community members come together to address health concerns in the Bronx.

The BRAID model
BRAID stands for Bridging Research, Accurate Information, and Dialogue
BRAID is an evidence-based biphasic model developed at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine. The model closely aligns with best practices in trustbuilding¹. The model represents a unique collaboration where clinical researchers, healthcare professionals, and community members come together to address health concerns in the Bronx.

The BRAID model
BRAID stands for Bridging Research, Accurate Information, and Dialogue
BRAID is an evidence-based biphasic model developed at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine. The model closely aligns with best practices in trustbuilding¹. The model represents a unique collaboration where clinical researchers, healthcare professionals, and community members come together to address health concerns in the Bronx.

¹Association of American Medical College Principles of Trustworthiness

BRAID first partners with local community-based organizations (CBOs) and faith-based organizations (FBOs) to help identify trusted community leaders to join the conversation.
The community experts are invited to participate in ongoing “Conversation Circles” with clinicians and scientists, around health issues that are important to them and their communities.

BRAID first partners with local community-based organizations (CBOs) and faith-based organizations (FBOs) to help identify trusted community leaders to join the conversation.
The community experts are invited to participate in ongoing “Conversation Circles” with clinicians and scientists, around health issues that are important to them and their communities.

BRAID first partners with local community-based organizations (CBOs) and faith-based organizations (FBOs) to help identify trusted community leaders to join the conversation.
The community experts are invited to participate in ongoing “Conversation Circles” with clinicians and scientists, around health issues that are important to them and their communities.
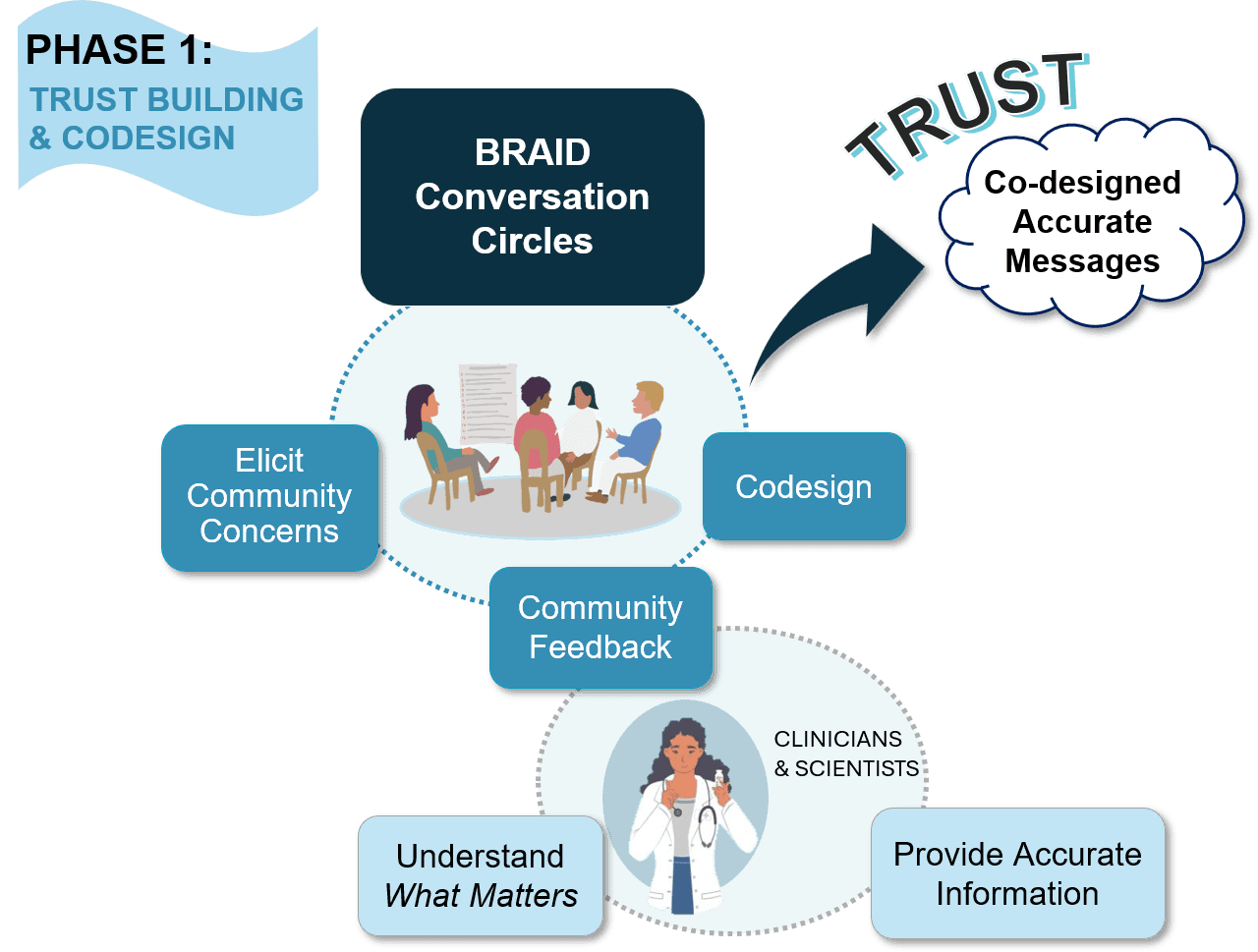
BRAID's first phase is about trust building & co-design
During phase one of the BRAID model, safe spaces called "Conversation Circles" are created for ongoing dialogue between trusted community messengers (Community Experts) and clinicians and scientists representing public health and/or health systems. Once a sense of trust is established, participants are supported as they work to co-create accurate health messages tailored for the local community.

BRAID's first phase is about trust building & co-design
During phase one of the BRAID model, safe spaces called "Conversation Circles" are created for ongoing dialogue between trusted community messengers (Community Experts) and clinicians and scientists representing public health and/or health systems. Once a sense of trust is established, participants are supported as they work to co-create accurate health messages tailored for the local community.

BRAID's first phase is about trust building & co-design
During phase one of the BRAID model, safe spaces called "Conversation Circles" are created for ongoing dialogue between trusted community messengers (Community Experts) and clinicians and scientists representing public health and/or health systems. Once a sense of trust is established, participants are supported as they work to co-create accurate health messages tailored for the local community.

BRAID's second phase is about message dissemination
In phase two of the BRAID model, trusted messengers are empowered to disseminate co-created health messages through their social networks. The process of sharing information is called “BRAIDing” and the trusted community messengers who share messaging are called “BRAIDers”. BRAIDers bring lessons learned about emerging community concerns and beliefs back to the Conversation Circles to inform the development of new health messages that address what matters to their community.

BRAID's second phase is about message dissemination
In phase two of the BRAID model, trusted messengers are empowered to disseminate co-created health messages through their social networks. The process of sharing information is called “BRAIDing” and the trusted community messengers who share messaging are called “BRAIDers”. BRAIDers bring lessons learned about emerging community concerns and beliefs back to the Conversation Circles to inform the development of new health messages that address what matters to their community.

BRAID's second phase is about message dissemination
In phase two of the BRAID model, trusted messengers are empowered to disseminate co-created health messages through their social networks. The process of sharing information is called “BRAIDing” and the trusted community messengers who share messaging are called “BRAIDers”. BRAIDers bring lessons learned about emerging community concerns and beliefs back to the Conversation Circles to inform the development of new health messages that address what matters to their community.
The diagram below puts the pieces of the dynamic BRAID model together
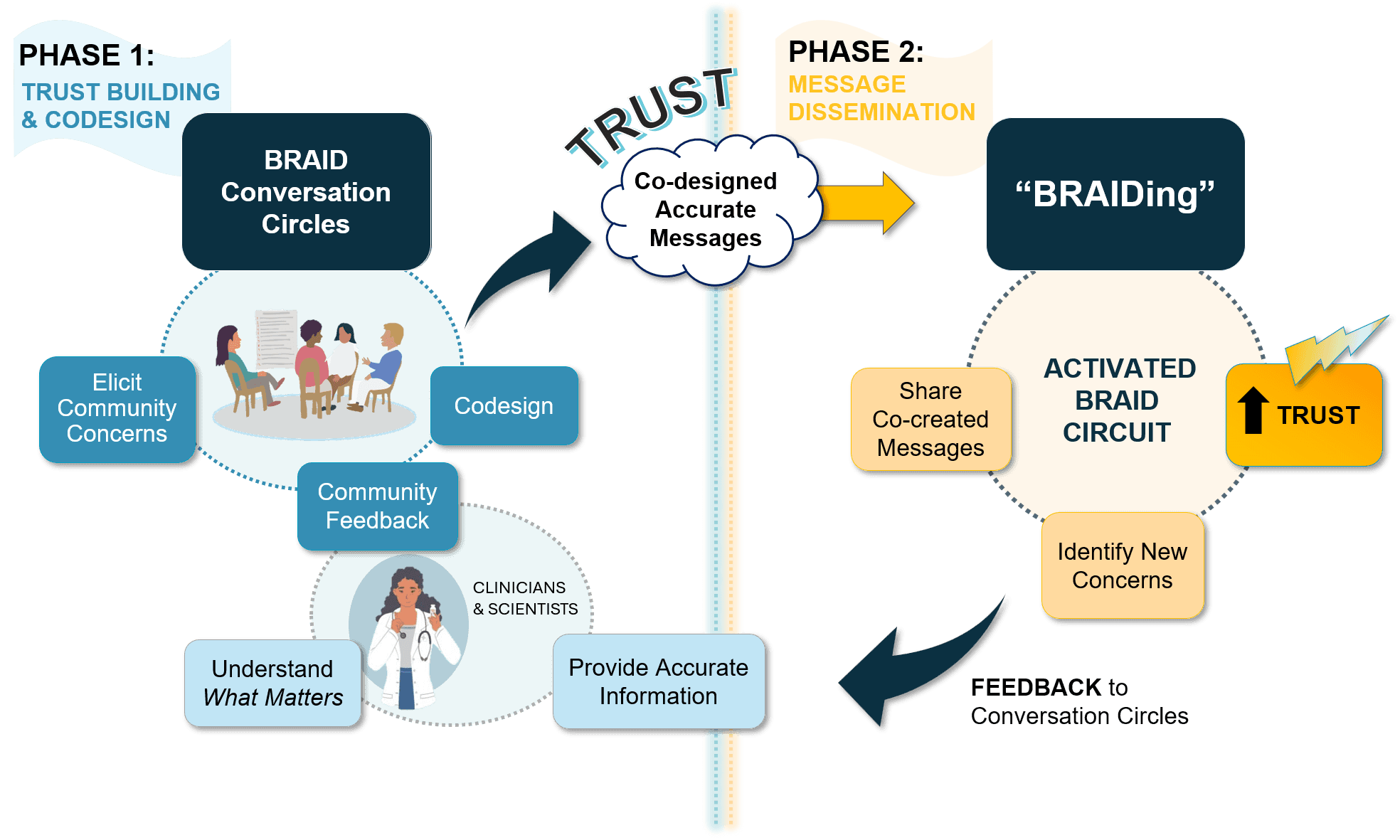
The diagram below puts the pieces of the dynamic BRAID model together

The diagram below puts the pieces of the dynamic BRAID model together


